Python-字符串
Published:
字符串
字符串基础
字符串是由独立字符组成的一个序列,通常包含在单引号(’‘)双引号 (”“)或者三引号之中(’’’ ‘'’或””” “”“,两者一样)
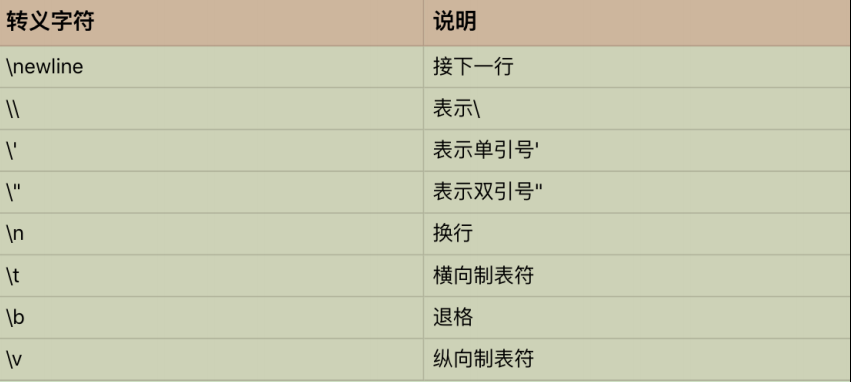
Python 也支持转义字符。所谓的转义字符,就是用反斜杠开头的字符串,来表示一些特定意义的字符。
Python 的字符串是不可变的(immutable)。因此,用下面的操作,来改变一个字符串内部的字符是错误的,不允许的。
s = 'hello'
s[0] = 'H'
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: 'str' object does not support item assignment
Python 中字符串的改变,通常只能通过创建新的字符串来完成。
s = 'H' + s[1:] # 方法一
s = s.replace('h', 'H') #方法二
常用操作
Python 的字符串同样支持索引,切片和遍历等等操作。
字符串常用的内置函数:
- string.join(iterable) 表示把每个元素都按照指定的格式连接起来。
- string.append(iter) 追加字符串
- string.split(separator) 表示把字符串按照 separator 分割成子字符串,并返回一个分割后子字符串组合的列表。
- string.strip(str),表示去掉首尾的 str 字符串;
- string.lstrip(str),表示只去掉开头的 str 字符串;
- string.rstrip(str),表示只去掉尾部的 str 字符串
字符串格式化
string.format(),就是所谓的格式化函数;而大括号{}就是所谓的格式符,用来为后面的真实值——变量预留位置。
print('no data available for person with id: {}, name: {}'.format(id, name))
字符串格式化还可以用 % 来表示。其中 %s 表示字符串型,%d 表示整型等等
print('no data available for person with id: %s, name: %s' % (id, name))
